EYELID PTOSIS
Overview
"Eyelid Ptosis" ( = "Blepharoptosis", or simply "Ptosis") is a disease represents trouble of opening eyelids, which can be occur from various causes. Particularly the junction between the muscle that lifts the eyelid and the eyelid itself is a weak point, and is structurally apt to elongate abnormally. Therefore, the eyelid ptosis is a popular disease that can occur to anybody. However, this disease does not cause eyelid drooping immediately, but initially causes symptoms that seems unrelated to the eyelid, such as headache, shoulder stiffness, and eye strain. Therefore, many people probably suffer from this annoying condition without knowing about this disease. Moreover, as the disease progresses, one cannot adequately open the eyes. This change interferes with "visibility", and off course, causes a lot of troubles in daily life.
Diagnosis
An only diagnosis of "You have ptosis" is not adequate.
There are various causes and degrees of eyelid ptosis.
Only after all of these concerns are complehensively diagnosed,
exact prospect of treatments can be assesed.
Therefore, the diagnosis requires advanced expertise.
It is noted that it takes about an hour to explain all these things.
We consider it most important that
the one who suspects ptosis first consult a doctor in order to understand the disease,
current conditions, and prospect of the treatment.
Check Points
If you suspect Ptosis? The followings are the check points for the purpose of self-diagnosis. Please check yourself.
Treatment
Treatment is by surgery.
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia.
There is no need of hospitalization. (Although possible if desired).
Immediately after the operation, the eyelids can be fully opened, and the
motion of eyelids are fully repaired.
In appearance, the eyelids changes from deformed eyelids to widely opened beautiful eyes.
The changes are often felt as "returning to the eyes of past self".
Additionally, headache, shoulder stiffness, and eyestrain are reduced in many cases.
†This kind of operation can be said as one of the most difficult operations in the field of plastic surgery. Skills and experiences are required to achieve an adequate, natural and beautiful result. In fact, one of the features of this disease is that, although undesirable, we often encounter inadequately operated cases. In our clinic, we also perform secondary repair of such cases, reaching to a considerable number of such operations.
Actual Cases Click photo to enlarge.
Click photo to enlarge.
If you imagine "surgery", you must feel "terrible" and hesitate about surgery. We are making efforts to perform "painless" treatment as far as possible, and have made various technical improvements. We also performs surgery in a meticulous manner to reduce postoperative swelling and pain to a minimal level. The cases herein represents the postoperative courses of such operations. Anyone who undergoes an operation is naturally apprehensive, and needs a lot of courage. We hope it could be a help for removing the fear of surgery to refer to the following concrete cases of surgery, even if it is a little bit.
Aponeurotic Ptosis, Moderate
Before The Operation
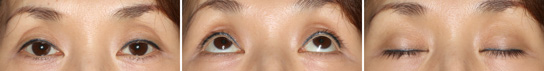
The grade of ptosis is light - medium. However, it is a difficult cases. The patient had been refused the operation by several doctors. The reason of difficulty is sever hollows.
Immediately After The Operation
This is just after the operation. The eyes are almost symmetrical. The hollow in the left eyelid still remains a little bit.
First Day After The Operation

This is at the next day after the operation. The swelling can be suppressed to a minimal level. In the cases of our clinic, the swelling usually reaches to the peak at the second or third day after the operation.
Fourth Day After The Operation (The Day At The Suture Removal)

This is at the forth day after the operation. The swelling seems to have past its peak. The sutures are removed and the wounds are not problematic. The elevation of the eyelids is adequate. Makeup is allowed, and may conceal the trace of operation.
First Month After The Operation

This is at the first month after the operation. Swelling almost disappears. The hollow on the left eyelid seems better. The wounds gradually become natural in 3 - 6 months.
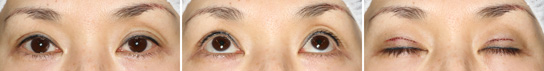
Aponeurotic Ptosis, Moderate
Before The Operation
The degree of ptosis is moderate to relatively severe. The double eyelid becomes rather widened. Hollows are mild. A Linear bulge similar to wheal are found in the upper part of both eyelids. This is due to fat injection for the purpose of correction of the hollow. However, as a treatment, it is apparently inadequate and we consider it should be repaired.
Immediately After The Operation

This is immediate after the operation. The repair of the eyelids are finished with minimal asymmetry. A blue spot, subcutaneous bleeding, is noted in the lateral part of the right upper eyelid. This is occasional, but unusual.
Second Day After The Operation
This is at the second day after the operation. The swelling have reached its peak. Although swelling is mild, the blue spot is changed to a reddish ecchymosis.
Fifth Day After The Operation (The Day At The Suture Removal)
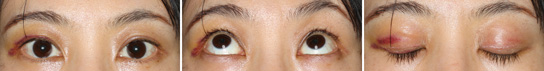
5 days are passed after the operation, and all the sutures are removed. Swelling begins to reduce. Ecchymosis remains a little longer. It becomes yellowish with fading reddness after two weeks, and disappears after 3 weeks. Because all the sutures are removed, ecchymosis can be covered with makeup.
First Month After The Operation
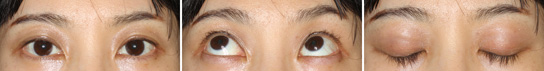
The ecchymosis disappears completely. Eyes are open adequately. There is little trace of surgery in such cases.
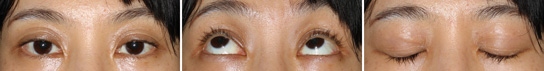
Aponeurotic Ptosis, Moderate
Before The Operation
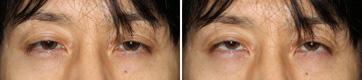
This is before the operation. Double-eyelid crease have became multiple. Also the width of the double-eyelid is increased. Although asymmetrical changes are slight, eyelids seem difficult to be opened. (He seemes not to look upwards very well.)
Immediately After The Operation
This is an immediate postoperative view. We operated to avoid swelling as far as possible. Within this level of swelling, even a trivial asymmetry can be immediately corrected. Eyelid swelling by operation may cause transient droop of the eyelid, which makes it difficult to adjust the level of the eyelid. He can look upwards adequately.
Third Month After The Operation
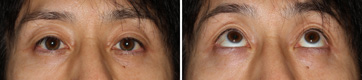
This is at the third month after the operation. He can look upwards appropriately. Eyestrain, headache and shoulder stiffness has been disappeared almost completely.
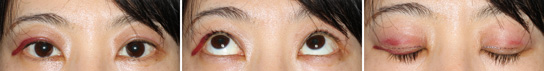
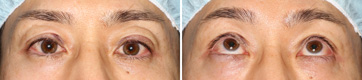
Aponeurotic Ptosis, Moderate
Before The Operation
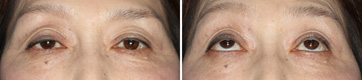
This is a moderate-to-severe aponeurotic ptosis. The lines of double-eyelid is widen and multiple. The right eyelid droops more than the left. She looks very hard to see upward direction. She felt eyestrain and shoulder stiffness.
Immediately After The Operation
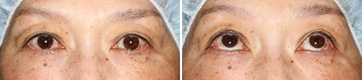
This is just postoperative view. The eyes are opened clearly. The right eyelid was adjusted to be over-corrected a little more than the left. If the eyelids swell more, it becomes difficult to adjust as such. She can look upwards correctly.
Third Month After The Operation
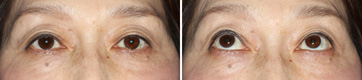
This is at the third month after the operation. The eyelids are settled down in natural form.
Aponeurotic Ptosis, Moderate
Before The Operation
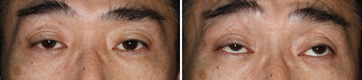
Relatively moderate to severe grade of aponeurotic ptosis. He seemes to have difficulty in looking upwards.
Immediately After The Operation
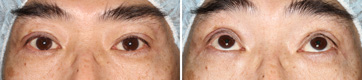
This is immediately after the operation. The levels of right and left eyelid were adjusted to be almost equal. He could gaze upward with ease.
Third Month After The Operation
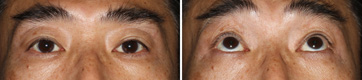
This is at the third month after the operation. The result is natural. He has been able to look upwards well.
Aponeurotic Ptosis, Severe
Before The Operation
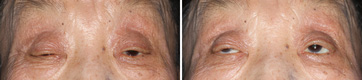
The patient is almost 80 years of age with ptosis. Her eyes were hardly opened due to ptosis. Therefore, she had a very difficulty in daily life. She came to our clinic with her family.
Immediately After The Operation
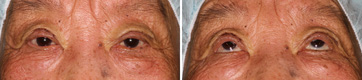
Just Postoperative view. The eyelids of elderly patient easily swell by the operative invasion. The operation should be performed without swelling of the eyelids as far as possible, otherwise, it will become difficult to compare the left and right eyelids. She became able to look upwards well.
Third Month After The Operation
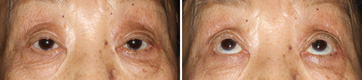
This is at the third month after the operation. She became capable of elevating eyelids sufficiently. She said she could go anywhere by herself. After the operation she came to our clinic by herself. The habit of elevating eyebrows still remained, but she did not feel any discomfort about it.
Left Congenital Ptosis, Right Aponeurotic Ptosis
Before The Operation
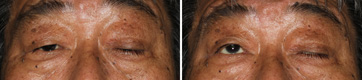
This is the patient with left congenital ptosis. In this patient, the function of eyelid-elevating muscle 'the levator muscle', was lost in born, therefore, on looking upwards, the left eyelid did not go up at all. If you pay close attention to the left eyebrow rising, you can see that he is trying to pull the left eyelid upwards. However, the pulling power did not reach the eyelid.
After The Transplantation of The Fascia Lata (Left)
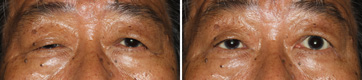
This is at the several months after the operation of fascia lata transplantation to the left eyelid. The fascia lata directly connected between the eyebrow and the eyelid, so he could rise the eyelid by a bit of elevating the eyebrow. Consequently, the latent aponeurotic ptosis of the right eyelid was disclosed. We consider that the power of elevating the right eyelid that had been put unconsciously before the operation has been released since the operation. (He seemed not to look upwards very well at that time.)
After The Ptosis Repair (Right)
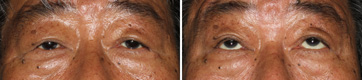
This is at the several months after the right ptosis operation. The balance of right and left eyelids lifting becomes adqueate. He can look upwards well.
Involutional Entropion
Involutional Entropion Of The Lower Eyelid
Before The Operation
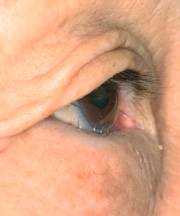
Pay close attention to the lower eyelid. Eyelash cannot be seen. The involutional entropion is caused by the relaxation of the surrounding eyelid-supportive tissues, and consequently. the eyelid turned inwards with eyelid skin and the eyelash contacting directly with eye surface. In this way the eyes are chronically injured, inflammatory, and reddish, with gums and tears accumulated at all times. This disease can be comparatively surely treated by operation. We adopted the modified Jones method. Applying this surgery, entropion hardly recurs. The patient can get the comfortable life back postoperatively.
First Month After The Operation
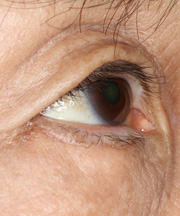
This is at the first month after the operation. Inverted skin and the eyelash comes outwards again clearly. The scar just under the eyelash was still visible, but would be better.
Third Month After The Operation
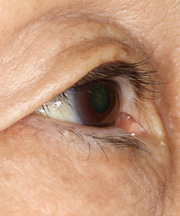
This is at the third month after the operation. The entropion has not recurred, and the scar under the eyelash becomes hardly visible. The patient is living in comfort.
All these photos are put up on this web site with the consent of the patient.








